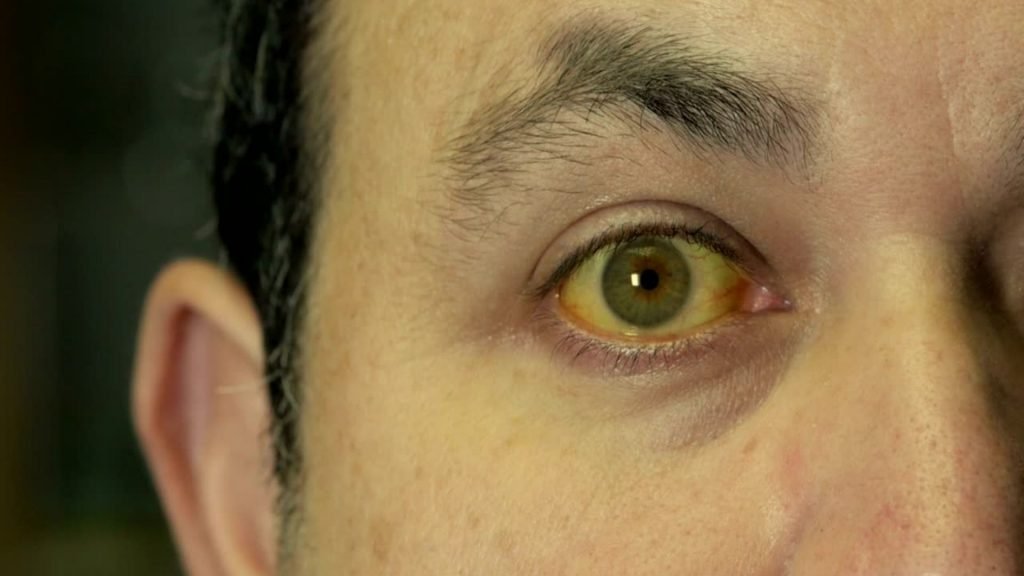
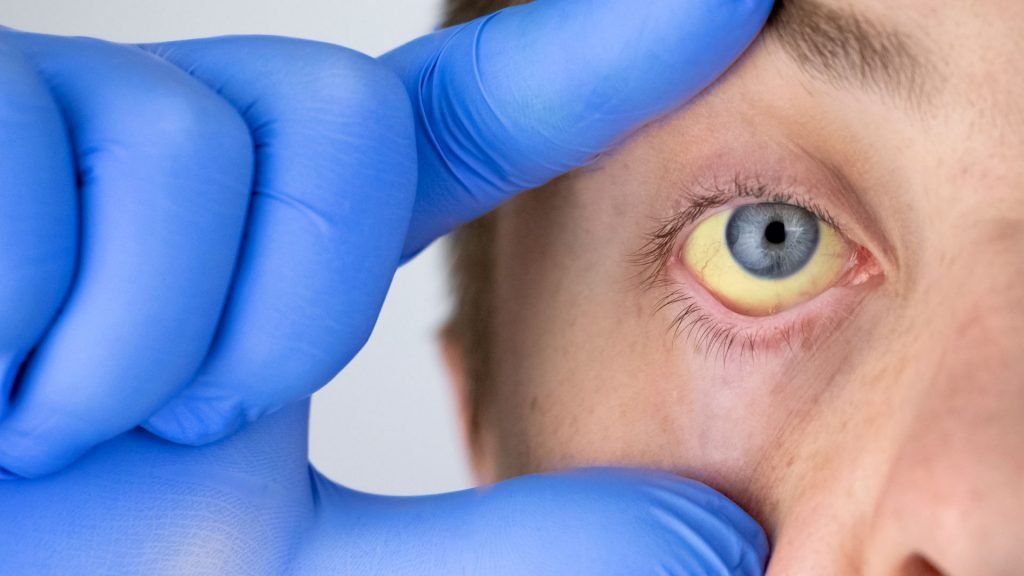
Jaundice is a term used to describe the yellow color of the skin, eyes white color, and body fluids. Often, the color of the skin and the white of the eyes vary from person to person. This is due to different levels of bilirubin, as high levels of bilirubin change skin color to yellow, and very high levels change the color to brown.
It also refers to a problem with the liver or bile ducts. It may occur to all people of all ages and may affect 60% of newborns as well.
The most famous of these symptoms are:
Mostly, a high level of bilirubin in the blood causes some symptoms which include:
If the cause of jaundice is a low level of bilirubin in the blood, it may lead to other symptoms, such as:
Newborns may show symptoms and signs within 72 hours of birth as the red blood cells in the baby’s body are broken down because the baby’s liver is less effective in purifying the body from bilirubin.
The following points explain the causes and risk factors for this disease:
Jaundice is often a sign of a problem with the liver. It is caused by the body’s inability to properly process bilirubin.
Bilirubin is yellow-colored waste that remains in the blood after iron is removed from the blood. The liver filters these waste products from the blood. When bilirubin reaches the liver, other substances stick to it. This is referred to as conjugated bilirubin. Conjugated bilirubin enters the bile and then exits the body.
But when bilirubin levels are high in the body, the liver becomes unable to get rid of it. A condition that leads to its deposition in nearby tissues. This phenomenon is called hyperbilirubinemia.
Some other, but rare, reasons may lead to the appearance of the disease in some people. The most prominent of these reasons are:
This is a genetic condition caused by a defect in the enzyme responsible for processing bilirubin.
This disease prevents the production of conjugated bilirubin from the liver cells.
This is a form of harmless jaundice. It occurs due to the high level of beta-carotene in the body, which leads to yellowing of the skin. It does not occur as a result of increased bilirubin.
Among the most popular factors that may lead to the risk of developing jaundice are:
It is due to the failure of the liver to conjugate and secrete bilirubin. This leads to its accumulation.
This inflammation causes bile secretion and bilirubin build-up, which leads to jaundice.
This prevents the liver from removing and eliminating bilirubin.
When a high percentage of red blood cells is broken down, the production of bilirubin increases.
It is a genetic disease that impairs the ability of enzymes to process bile secretion.
Cholestasis is a disease that stops the flow of bile from the liver. This causes conjugated bilirubin that contains bile to remain in the liver instead of being excreted.
This is a disease that affects newborns who suffer from jaundice. If not treated, it. leads to permanent brain damage to the child.
Complications of jaundice occur because of the underlying problem and are not linked to it. The most prominent of these complications include:

Sometimes the itching associated with jaundice may be severe in some people. This often leads to scratching the skin, insomnia, or suicidal thoughts.
A lack of vitamins necessary for blood clotting leads to blockage of the bile duct, which may result in jaundice.
Below, you will find six ways to diagnose this disease.
The doctor checks the patient’s history and diagnoses jaundice by getting information about the symptoms that the patient suffers from. He also examines the abdomen and makes sure that the liver is so solid.
Often, your doctor will recommend a liver function test to check whether your liver is working properly.
If your doctor can’t find the cause of the disease, he may recommend blood tests to check bilirubin levels and blood composition. These tests will include:
This test measures levels of unconjugated bilirubin. A normal level for adults and older children should be between 0.3 and 0.6 mg/dl.
This test measures the level of red blood cells, white blood cells, and blood platelets.
Your doctor will recommend hepatitis A, B, and C tests.
If your doctor suspects a blockage, he or she may recommend imaging tests, such as an MRI, CT scan, and Ultrasound scan to check the structure of your liver.
Your doctor may perform endoscopic imaging of the pancreas and cholangiography. This procedure also combines endoscopy and X-ray imaging.

This procedure is done by inserting a needle into the liver to obtain a sample of liver tissue and then examining it under a microscope, to confirm whether the patient suffers from inflammation, cirrhosis of the liver, fatty liver, or cancer.
The treatments of this disease depend on its cause. They target the cause, not the symptoms. The most used treatments are:
Jaundice can sometimes be the result of anemia. So one should often increase iron levels in the blood either by iron supplementation or by eating foods rich in iron.
If jaundice is due to an infection, we often treat it by giving the patient antiviral or steroid medications.
Sometimes, it is a bile duct obstruction that causes jaundice. In this case, the doctor resorts to surgical intervention to remove this blockage.
It is important to maintain the health of the liver as this disease is related to liver function. This is done through:
There are three main types of jaundice. They are:
In this case, jaundice occurs as a result of a problem or disease in the liver which affects the hepatocytes.
It may occur as a result of hemolysis or a severe reduction in red blood cells, which in turn leads to increased production of bilirubin.
One of the well-known types of this disease is obstructive jaundice. It occurs from the obstruction of the bile duct, which leads to the accumulation of bilirubin in the liver.
Leave a comment